Nothing is for sale here. Freewill tips keep the site running. Want to help? → Tip via Paypal
Display Style
If you think of HTML elements as blocks of content it can help you to understand the structure of a web page. These blocks have a default value of inline or block. These can be modified in one of several ways. Before we get to that, take a look at this image depicting how inline and block elements are displayed.
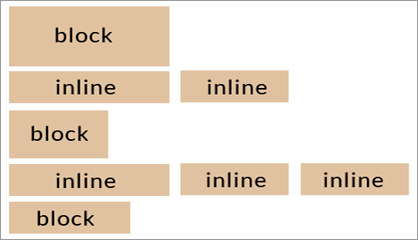
A block-level element always creates an empty line above and below itself. It runs the width of the parent element, whether the content fills the entire space or not. A heading is an example of a block level element. No other content is on the same line unless the display property has been changed. You can see in the image that each block level element is on a line by itself.
An inline-level element is displayed on a line taking up only as much horizontal room as it needs. Other inline elements can follow in the same line until the horizontal space is consumed, at which point it will continue on the next line. Unlike the block-level element, when it drops to a new line it doesn't create an empty line above or below itself. A span element is an example of an inline element.
The display property of any element can be changed. Here's an example:
by Betty Kister
If you coded a heading tag with that, the author name would be on the same line as the story title. If the display property wasn't changed, there would be an empty line below the story title and the author's name after that.
Here are the available display property values and what they mean:
- block:
- Elements with display: block are rendered as block-level elements. They take up the full width of the parent container by default and create a line break before and after the element.
- inline:
- Elements with display: inline are rendered as inline-level elements. They do not create line breaks and only take up as much space as necessary to display their content. You cannot apply height and width properties to inline-level elements as you can with block-level elements.
- inline-block:
- Elements with display: inline-block are a mix of block-level and inline-level elements. They do not create line breaks and can have specified width and height values and honor top and bottom margins and padding. This value is often used for horizontal menus.
- none:
- Elements with display: none are completely removed from the page layout. They are not rendered and do not occupy any space. This is often used to hide elements dynamically using JavaScript.
- flex:
- Elements with display: flex create a flex container that allows you to easily create flexible and responsive layouts. It enables a flexible box model where child elements (flex items) can be arranged horizontally or vertically.
- grid:
- Elements with display: grid create a grid container that allows you to create complex two-dimensional layouts. It provides powerful grid-based alignment and positioning capabilities for its child elements.





